Additive Manufacturing
- By Grace Esther, Outreach
This blog is going to give you a wide range of clarity on additive manufacturing, its scope, where it has been used, and the facilities to perform the same @VIT.
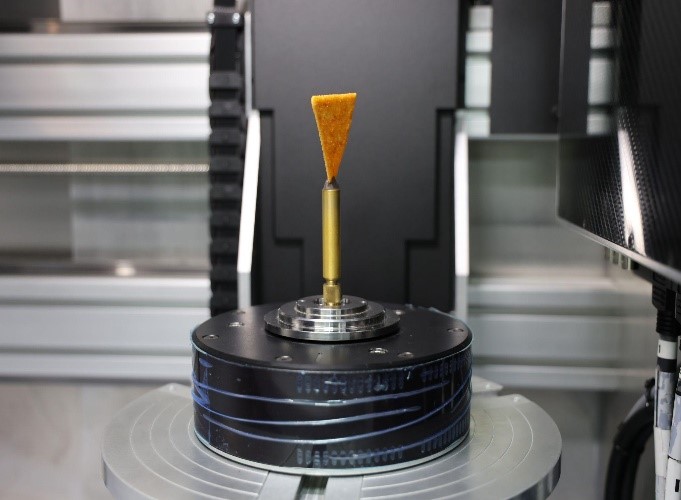
Diving into any concept will ultimately raise the first question of what is the technology all about and here’s the answer to it. Additive Manufacturing (AM) refers to a process by which digital 3D design data is used to build up a component in layers by depositing material. The term “additive manufacturing” refers to the creation of objects by adding materials. Thus, when an object is created by adding material rather than removing it (subtractive manufacturing) it is considered additive manufacturing.
We all would have a great thought on why the industries adopt additive manufacturing rather than sticking to the traditional methodologies that have been used so far. One main reason is any industry has to cope up with the changes and upgrade themselves to the advancement in the technologies that happens in the fast moving world. Moreover, by using additive manufacturing, each item can be tailored to specific requirements without incurring additional tooling costs or production delays, which in other words can be said to get greater production by cost cutting the expenses on the raw materials. Further, AM processes generate minimal waste material since they add material selectively and by using only what is necessary to build the object. AM is cost-effective and easy to set up since industries can design and produce their products using a single device. However, in traditional manufacturing, a whole factory has to be set up which involves a lot of investment.
Having said that additive manufacturing is very affordable in nature, can every industry implement it or does the manufacturing methodology be restricted to specific industries? Some of the potential industries that have implemented the Additive Manufacturing technique are Aerospace, automotive, dental, tool or mold making, implants, electronics, sports equipment, prosthetics, surgical devices. Recently, ISRO used a 3D printed rocket engine in PSLV in collaboration with Wipro3D, Bangalore. But does that restrict the usage of additive manufacturing, NO. The viabilities is yet researched for the methodology to be implemented in other industries too.
Here are a few industries that have successfully used additive manufacturing:
- Recently, ISRO used a 3D printed rocket engine in PSLV in collaboration with Wipro3D, Bangalore.
- RMIT University creates new 3D printed titanium metamaterial that shows “supernatural strength”
- 3D printed fuel nozzle by GE
- 3D Printing Titanium in Aerospace Manufacturing Applications
- Metal 3D printed water connectors for the Audi W12 engine
- Applications in medical industry
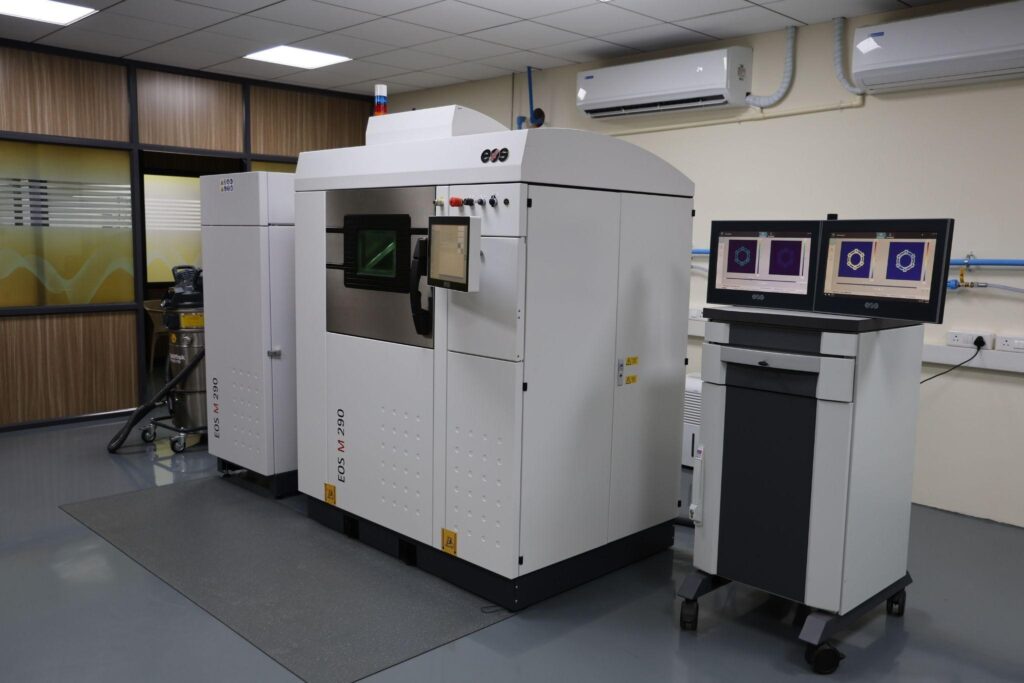
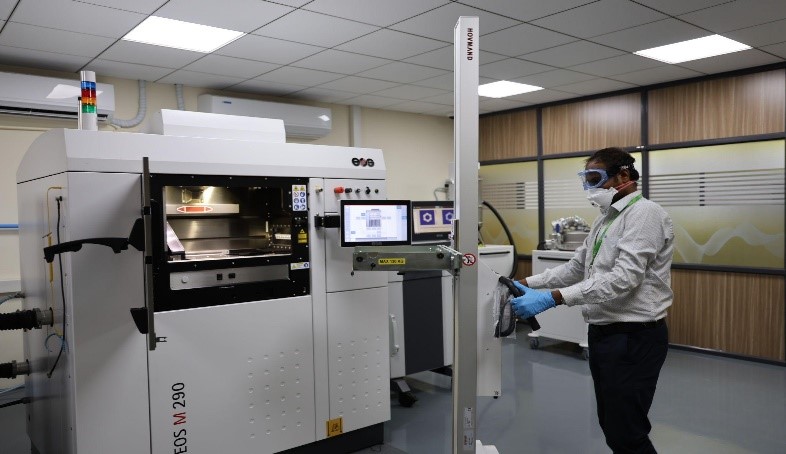
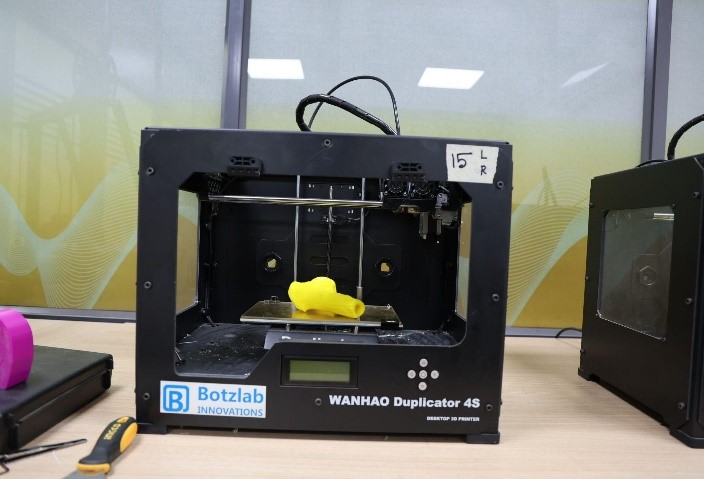
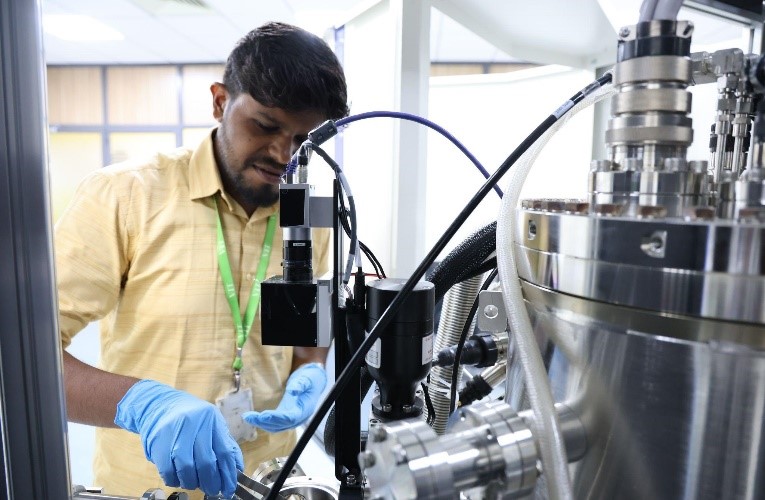
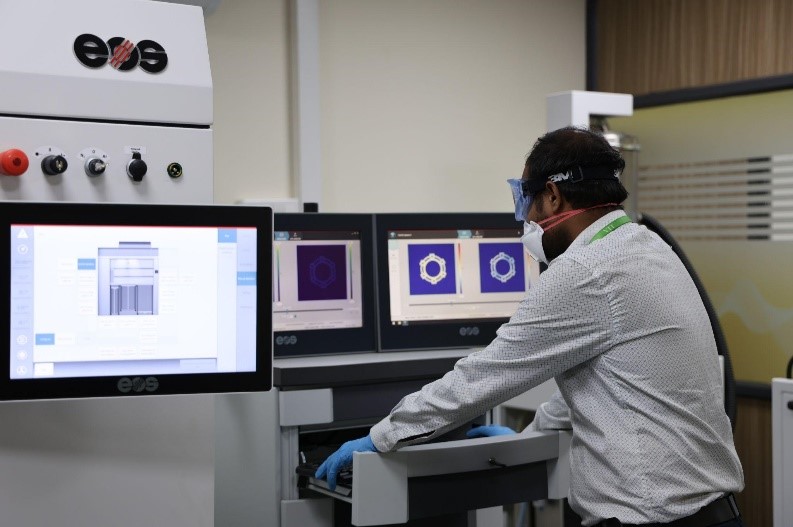
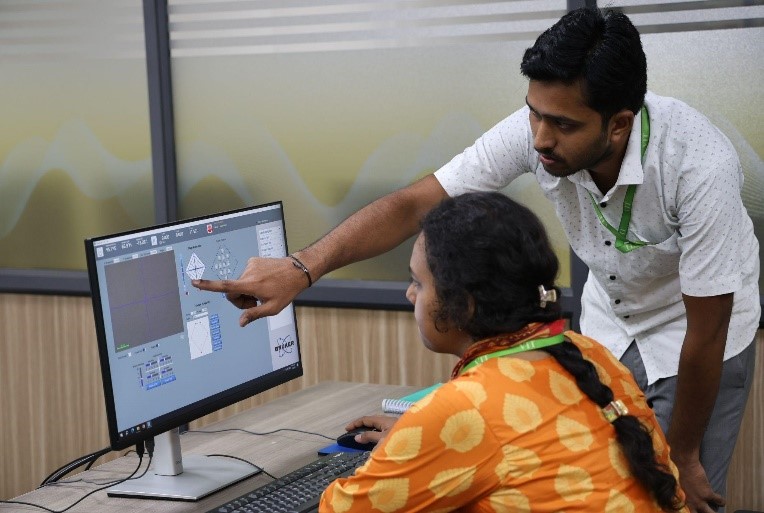
Now let’s travel in the memory lane and get a quick history on how this additive manufacturing lab has been set up at VIT. A proposal entitled “Additive Manufacturing for Fostering Transdisciplinary Research” submitted by Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore, India was approved by DST under Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence scheme with a total budget of Rs. 21.3936 Cr., Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with focus to develop indigenous patient specific bio-implants for health care and flexible solar cells for Cleaner Energy production using additive manufacturing technologies is the main theme of the PURSE lab at VIT. Also, these technologies will be explored to develop niche components using multi-functional materials for aerospace/defense applications.
VIT also has greater expertise in handling these equipment including both the faculty members and the research scholars.
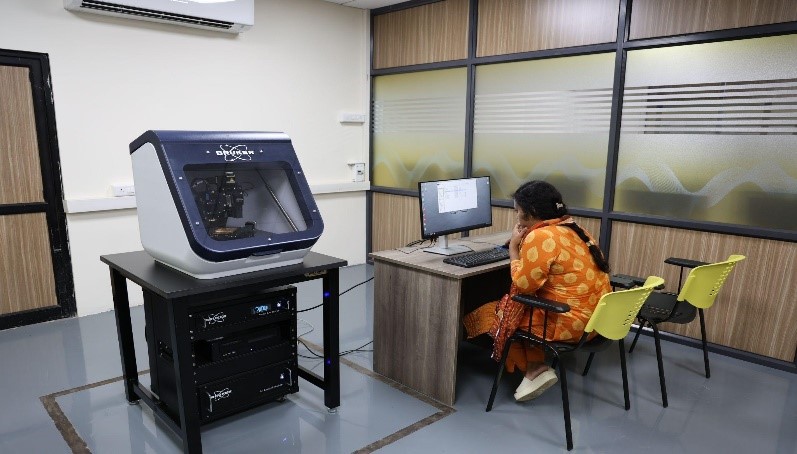
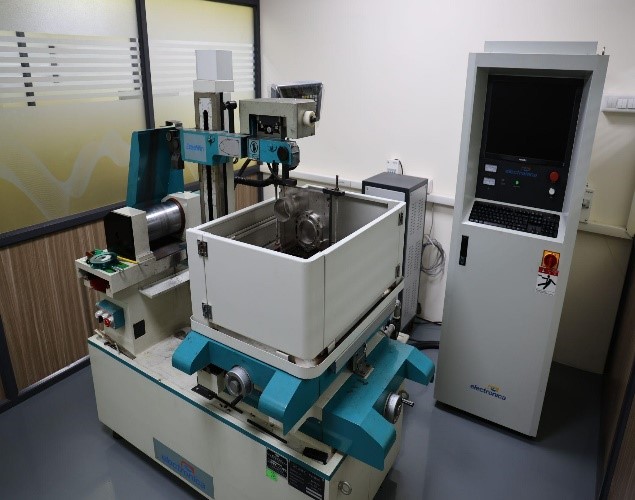
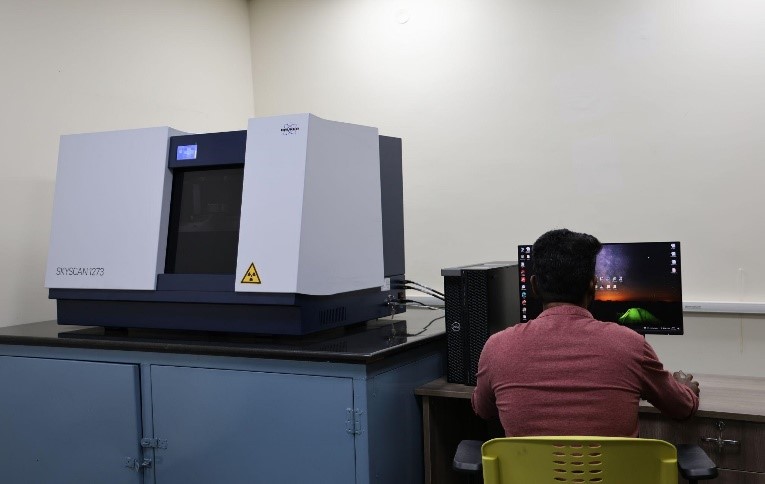
Some of the facilities at VIT also include:
| Sl.No | Equipment Name |
| 1 | Metal 3D Printer |
| 2 | Tribo Nano indenter |
| 3 | Micro X-Ray CT Scanner |
| 4 | X-Ray Photo Electron Spectrometer (XPS) |
| 5 | Roll to Roll Die Coating with Drying & Lamination |
| 6 | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| 7 | Inkjet Printer* |
| 8 | Hot Isostatic Press** |
*Expected to be delivered by July’24 **Expected to be delivered by Oct’24
More than 20 faculty members and 30 research scholars are working in the areas of additive manufacturing such as new materials development, processing, characterization for aerospace, defense, automotive and medical applications from various disciplines of Mechanical Engineering, Design and Automation, Advanced Sciences, Chemistry, Nanotechnology, Innovative Manufacturing Research, Biomaterials, Cellular and Molecular Theranostics.

A detailed technical description has been given on the PURSE Lab Website: https://vit.ac.in/purse/
VIT warmly welcomes any interested UG, PG and Ph.D research scholars to utilize the facilities along with the industries. You can contact Dr.R.Vasudevan, Professor & PURSE Coordinator, School of Mechanical Engineering, VIT via call on 0416-2202207 / +91 9500027238 or you can drop a mail to vasudevan.r@vit.ac.in